コンピューティングのためのCUDAランタイムAPIの使用。CPUとGPUコンピューティングの比較
この記事では、CPUとGPUでC ++で記述されたアルゴリズムの実行を比較することにしました(サポートされているNvidiaGPUでNvidiaCUDAランタイムAPIを使用して計算を実行します)。CUDA APIを使用すると、GPUでいくつかの計算を実行できます。CUDAを使用してC ++ファイルがあります.cuの拡張子を。
アルゴリズムを以下に示します。
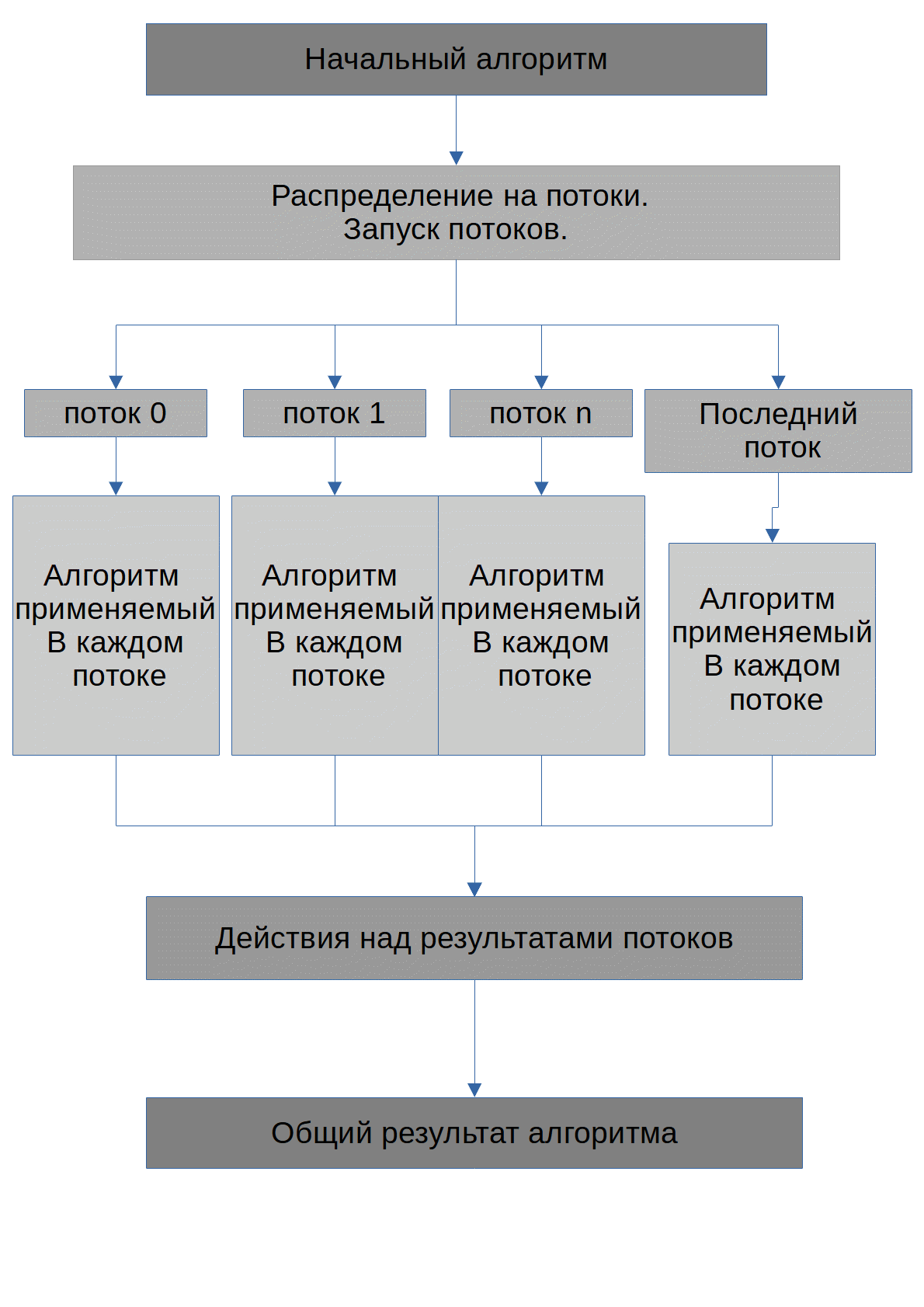
アルゴリズムのタスクは、可能な数Xを見つけることです。次数に上げると、初期数max_numberが取得されます。GPUに送信されるすべての番号がアレイに格納されることにすぐに注意します。各スレッドによって実行されるアルゴリズムは次のようになります。
int degree_of=2;
int degree_of_max=Number_degree_of_max[0];//
int x=thread;//
int max_number=INPUT[0];// ,
int Number=1;
int Degree;
bool BREAK=false;// while
while(degree_of<=degree_of_max&&!BREAK){
Number=1;
for(int i=0;i<degree_of;i++){
Number*=x;
Degree=degree_of;
}
if(Number==max_number){
OUT_NUMBER[thread]=X;//OUT_NUMBER Degree
OUT_DEGREE[thread]=Degree;// OUT_DEGREE X
}
degree_of++;
// :
if(degree_of>degree_of_max||Number>max_number){
BREAK=true;
}
}
CPU C ++で実行するコード。Cpp
#include <iostream>
#include<vector>
#include<string>// getline
#include<thread>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
int Running_thread_counter = 0;
void Upload_to_CPU(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max, int THREAD);
void Upload_to_CPU(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max, int THREAD) {
int thread = THREAD;
Running_thread_counter++;
unsigned long long MAX_DEGREE_OF = max[0];
int X = thread;
unsigned long long Calculated_number = 1;
unsigned long long DEGREE_OF = 2;
unsigned long long INP = INPUT[0];
Stop[thread] = false;
bool BREAK = false;
if (X != 0 && X != 1) {
while (!BREAK) {
if (DEGREE_OF <= MAX_DEGREE_OF) {
Calculated_number = 1;
for (int counter = 0; counter < DEGREE_OF; counter++) {
Calculated_number *= X;
}
if (Calculated_number == INP) {
Stepn[thread] = DEGREE_OF;
Number[thread] = X;
Stop[thread] = true;
BREAK = true;
}
DEGREE_OF++;
}
else { BREAK = true; }
}
}
}
void Parallelize_to_threads(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max, int size);
int main()
{
int size = 1000;
unsigned long long *Number = new unsigned long long[size], *Degree_of = new unsigned long long[size];
unsigned long long *Max_Degree_of = new unsigned long long[1];
unsigned long long *INPUT_NUMBER = new unsigned long long[1];
Max_Degree_of[0] = 7900;
INPUT_NUMBER[0] = 216 * 216 * 216;
ifstream inp("input.txt");
if (inp.is_open()) {
string t;
vector<unsigned long long>IN;
while (getline(inp, t)) {
IN.push_back(stol(t));
}
INPUT_NUMBER[0] = IN[0];//
Max_Degree_of[0] = IN[1];//
}
else {
ofstream error("error.txt");
if (error.is_open()) {
error << "No file " << '"' << "input.txt" << '"' << endl;
error << "Please , create a file" << '"' << "input.txt" << '"' << endl;
error << "One read:input number" << endl;
error << "Two read:input max stepen" << endl;
error << "." << endl;
error.close();
INPUT_NUMBER[0] = 1;
Max_Degree_of[0] = 1;
}
}
// ,
//cout << INPUT[0] << endl;
bool *Elements_that_need_to_stop = new bool[size];
Parallelize_to_threads(Number, Degree_of, Elements_that_need_to_stop, INPUT_NUMBER, Max_Degree_of, size);
vector<unsigned long long>NUMBER, DEGREEOF;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (Elements_that_need_to_stop[i]) {
if (Degree_of[i] < INPUT_NUMBER[0] && Number[i] < INPUT_NUMBER[0]) {//
NUMBER.push_back(Number[i]);
DEGREEOF.push_back(Degree_of[i]);
}
}
}
// ,
//
/*
for (int f = 0; f < NUMBER.size(); f++) {
cout << NUMBER[f] << "^" << DEGREEOF[f] << "=" << INPUT_NUMBER[0] << endl;
}
*/
ofstream out("out.txt");
if (out.is_open()) {
for (int f = 0; f < NUMBER.size(); f++) {
out << NUMBER[f] << "^" << DEGREEOF[f] << "=" << INPUT_NUMBER[0] << endl;
}
out.close();
}
}
void Parallelize_to_threads(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max, int size) {
thread *T = new thread[size];
Running_thread_counter = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
T[i] = thread(Upload_to_CPU, Number, Stepn, Stop, INPUT, max, i);
T[i].detach();
}
while (Running_thread_counter < size - 1);//
}
アルゴリズムが機能するには、初期番号と最大次数のテキストファイルが必要です。
GPU計算を行うためのコードC ++。Cu
// cuda_runtime.h device_launch_parameters.h
// cyda
#include "cuda_runtime.h"
#include "device_launch_parameters.h"
#include<vector>
#include<string>// getline
#include <stdio.h>
#include<fstream>
using namespace std;
__global__ void Upload_to_GPU(unsigned long long *Number,unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT,unsigned long long *max) {
int thread = threadIdx.x;
unsigned long long MAX_DEGREE_OF = max[0];
int X = thread;
unsigned long long Calculated_number = 1;
unsigned long long Current_degree_of_number = 2;
unsigned long long Original_numberP = INPUT[0];
Stop[thread] = false;
bool BREAK = false;
if (X!=0&&X!=1) {
while (!BREAK) {
if (Current_degree_of_number <= MAX_DEGREE_OF) {
Calculated_number = 1;
for (int counter = 0; counter < Current_degree_of_number; counter++) {
Calculated_number *=X;
}
if (Calculated_number == Original_numberP) {
Stepn[thread] = Current_degree_of_number;
Number[thread] = X;
Stop[thread] = true;
BREAK = true;
}
Current_degree_of_number++;
}
else { BREAK = true; }
}
}
}
cudaError_t Configure_cuda(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Stepn, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max,unsigned int size);
int main()
{
int size = 1000;
unsigned long long *Number=new unsigned long long [size], *Degree_of=new unsigned long long [size];
unsigned long long *Max_degree_of = new unsigned long long [1];
unsigned long long *INPUT_NUMBER = new unsigned long long [1];
Max_degree_of[0] = 7900;
ifstream inp("input.txt");
if (inp.is_open()) {
string text;
vector<unsigned long long>IN;
while (getline(inp, text)) {
IN.push_back( stol(text));
}
INPUT_NUMBER[0] = IN[0];
Max_degree_of[0] = IN[1];
}
else {
ofstream error("error.txt");
if (error.is_open()) {
error<<"No file "<<'"'<<"input.txt"<<'"'<<endl;
error<<"Please , create a file" << '"' << "input.txt" << '"' << endl;
error << "One read:input number" << endl;
error << "Two read:input max stepen" << endl;
error << "." << endl;
error.close();
INPUT_NUMBER[0] = 1;
Max_degree_of[0] = 1;
}
}
bool *Elements_that_need_to_stop = new bool[size];
// cuda
cudaError_t cudaStatus = Configure_cuda(Number, Degree_of, Elements_that_need_to_stop, INPUT_NUMBER, Max_degree_of, size);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addWithCuda failed!");
return 1;
}
vector<unsigned long long>NUMBER, DEGREEOF;
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
if (Elements_that_need_to_stop[i]) {
NUMBER.push_back(Number[i]);//
DEGREEOF.push_back(Degree_of[i]);//
}
}
// ,
/*
for (int f = 0; f < NUMBER.size(); f++) {
cout << NUMBER[f] << "^" << DEGREEOF[f] << "=" << INPUT_NUMBER[0] << endl;
}*/
ofstream out("out.txt");
if (out.is_open()) {
for (int f = 0; f < NUMBER.size(); f++) {
out << NUMBER[f] << "^" << DEGREEOF[f] << "=" << INPUT_NUMBER[0] << endl;
}
out.close();
}
//
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceReset();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceReset failed!");
return 1;
}
return 0;
}
cudaError_t Configure_cuda(unsigned long long *Number, unsigned long long *Degree_of, bool *Stop,unsigned long long *INPUT, unsigned long long *max,unsigned int size) {
unsigned long long *dev_Number = 0;
unsigned long long *dev_Degree_of = 0;
unsigned long long *dev_INPUT = 0;
unsigned long long *dev_Max = 0;
bool *dev_Elements_that_need_to_stop;
cudaError_t cudaStatus;
// GPU
cudaStatus = cudaSetDevice(0);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaSetDevice failed! Do you have a CUDA-capable GPU installed?");
goto Error;
}
//
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_Number, size * sizeof(unsigned long long));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!dev_Number");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_Degree_of, size * sizeof(unsigned long long));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!dev_Degree_of");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_Max, size * sizeof(unsigned long long int));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!dev_Max");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_INPUT, size * sizeof(unsigned long long));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!dev_INPUT");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMalloc((void**)&dev_Elements_that_need_to_stop, size * sizeof(bool));
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMalloc failed!dev_Stop");
goto Error;
}
// GPU
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_Max, max, size * sizeof(unsigned long long), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(dev_INPUT, INPUT, size * sizeof(unsigned long long), cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Upload_to_GPU<<<1, size>>>(dev_Number, dev_Degree_of, dev_Elements_that_need_to_stop, dev_INPUT, dev_Max);
//
cudaStatus = cudaGetLastError();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "addKernel launch failed: %s\n", cudaGetErrorString(cudaStatus));
goto Error;
}
// ,
cudaStatus = cudaDeviceSynchronize();
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaDeviceSynchronize returned error code %d after launching addKernel!\n", cudaStatus);
goto Error;
}
// GPU
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(Number, dev_Number, size * sizeof(unsigned long long), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(Degree_of, dev_Degree_of, size * sizeof(unsigned long long), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
cudaStatus = cudaMemcpy(Stop, dev_Elements_that_need_to_stop, size * sizeof(bool), cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost);
if (cudaStatus != cudaSuccess) {
fprintf(stderr, "cudaMemcpy failed!");
goto Error;
}
Error:// GPU
cudaFree(dev_INPUT);
cudaFree(dev_Degree_of);
cudaFree(dev_Max);
cudaFree(dev_Elements_that_need_to_stop);
cudaFree(dev_Number);
return cudaStatus;
}
識別子
__global__ CUDA APIを使用するには、関数を呼び出す前に、アレイ用にメモリを予約し、要素をGPUメモリに転送する必要があります。これによりコードの量は増えますが、計算はGPUで実行されるため、CPUの負荷を軽減できます。したがって、cudaは、少なくともcudaを使用しない他のワークロードのプロセッサをオフロードする機能を提供します。
cudaの例の場合、プロセッサのタスクは、GPUに命令をロードし、GPUからの結果を処理することだけです。CPUのコード内にある間、プロセッサは各スレッドを処理します。cydaには起動できるスレッドの数に制限があるため、両方のアルゴリズムで1000に等しい同じスレッド数を使用したことは注目に値します。また、CPUの場合は、変数を使用しました。
int Running_thread_counter = 0;すでに実行されたスレッドの数をカウントし、すべてのスレッドが実行されるまで待機します。
テスト構成
CUDA GPU-Z
- CPU:amd ryzen 5 1400(4core、8thread)
- RAM:8GB DDR4 2666
- GPU:Nvidia rtx 2060
- OS:windows 10 version 2004
- Cuda:
- Compute Capability 7.5
- Threads per Multiprocessor 1024
- CUDA 11.1.70
- GPU-Z:version 2.35.0
- Visual Studio 2017
CUDA GPU-Z
アルゴリズムをテストするために、私は使用しました
次のC#コード
は、初期データを含むファイルを作成し、CPUまたはGPUを使用してアルゴリズムのexeファイルを順番に起動し、それらの操作の時間を測定し、この時間とアルゴリズムの結果をファイルresult.txtに入力しました。Windowsタスクマネージャを使用して、プロセッサの負荷を測定しました。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using System.Diagnostics;
using System.IO;
namespace ConsoleAppTESTSTEPEN_CPU_AND_GPU_
{
class Program
{
static string Upload(Int64 number,Int64 degree_of)
{
string OUT = "";
string[] Chord_values = new string[2];
Int64 Degree_of = degree_of;
Int64 Number = number;
Chord_values[0] = Number.ToString();
Chord_values[1] = Degree_of.ToString();
File.WriteAllLines("input.txt", Chord_values);//
OUT+="input number:" + Number.ToString()+"\n";
OUT+="input degree of number:" + Degree_of.ToString()+"\n";
DateTime running_CPU_application = DateTime.Now;//
Process proc= Process.Start("ConsoleApplication29.exe");//exe c++ x64 CPU
while (!proc.HasExited) ;//
DateTime stop_CPU_application = DateTime.Now;//
string[]outs = File.ReadAllLines("out.txt");//
File.Delete("out.txt");
OUT+="CPU:"+"\n";
if (outs.Length>0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outs.Length; j++)
{
OUT+=outs[j]+"\n";
}
}
else { OUT+="no values"+"\n"; }
OUT+="running_CPU_application:" + running_CPU_application.ToString()+"\n";
OUT+="stop_CPU_application:" + stop_CPU_application.ToString()+"\n";
OUT+="GPU:"+"\n";
// korenXN.exe x64 GPU
DateTime running_GPU_application = DateTime.Now;
Process procGPU = Process.Start("korenXN.exe");
while (!procGPU.HasExited) ;
DateTime stop_GPU_application = DateTime.Now;
string[] outs2 = File.ReadAllLines("out.txt");
File.Delete("out.txt");
if (outs2.Length > 0)
{
for (int j = 0; j < outs2.Length; j++)
{
OUT+=outs2[j]+"\n";
}
}
else { OUT+="no values"+"\n"; }
OUT+="running_GPU_application:" + running_GPU_application.ToString()+"\n";
OUT+="stop_GPU_application:" + stop_GPU_application.ToString()+"\n";
return OUT;//
}
static void Main()
{
Int64 start = 36*36;//
Int64 degree_of_strat = 500;//
int size = 20-5;//
Int64[] Number = new Int64[size];//
Int64[] Degree_of = new Int64[size];//
string[]outs= new string[size];//
for (int n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
if (n % 2 == 0)
{
Number[n] = start * start;
}
else
{
Number[n] = start * degree_of_strat;
Number[n] -= n + n;
}
start += 36*36;
Degree_of[n] = degree_of_strat;
degree_of_strat +=1000;
}
for (int n = 0; n < size; n++)
{
outs[n] = Upload(Number[n], Degree_of[n]);
Console.WriteLine(outs[n]);
}
System.IO.File.WriteAllLines("result.txt", outs);// result.txt
}
}
}
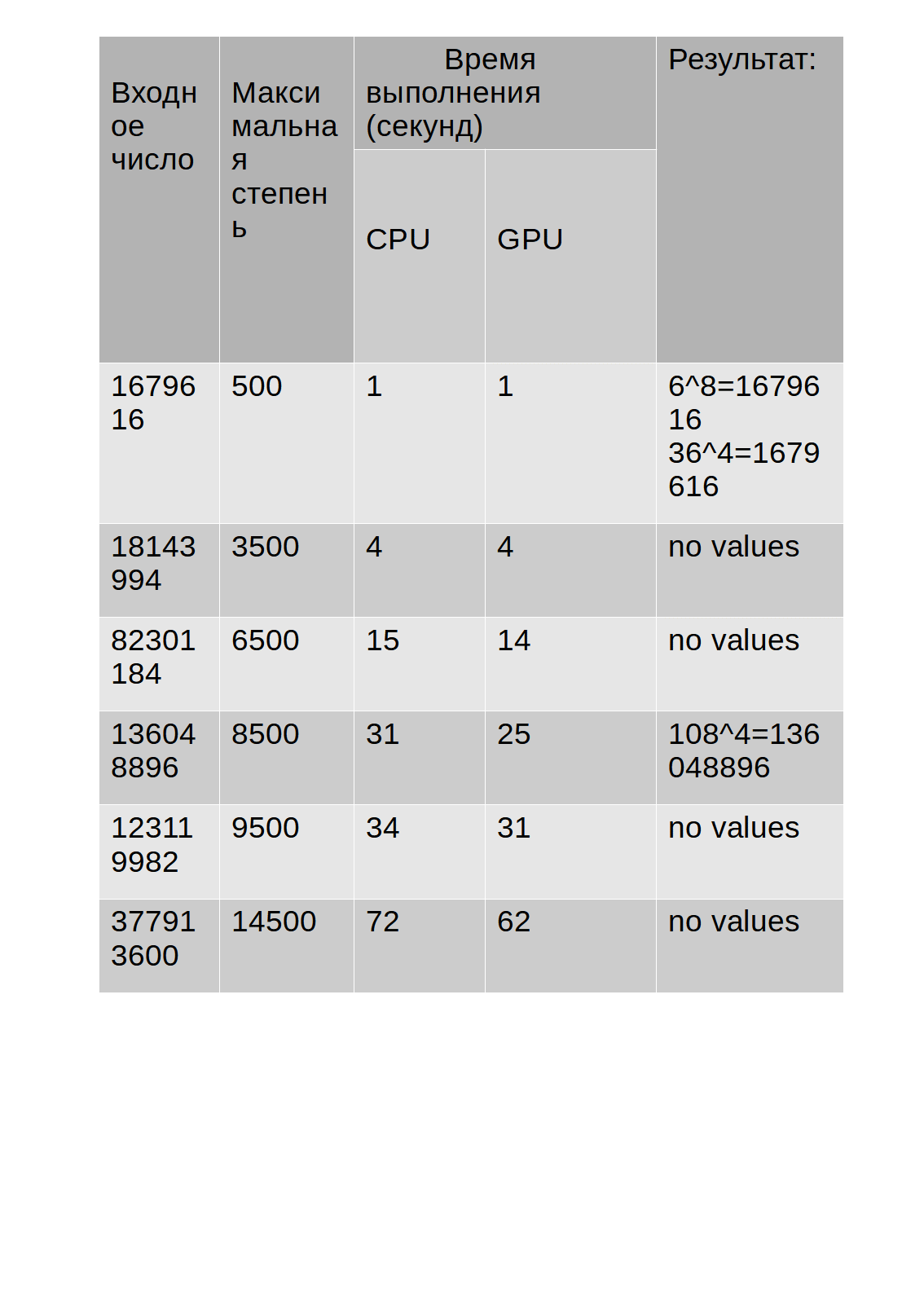
テスト結果を表に示します。

表からわかるように、GPUでのアルゴリズムの実行時間はCPUよりもわずかに長くなっています。
ただし、計算にGPUを使用するアルゴリズムの操作中に、タスクマネージャーに表示されるCPU負荷は30%を超えませんでしたが、計算にCPUを使用するアルゴリズムは68〜85%負荷しました。その結果、他のアプリケーションの速度が低下することがありました。また、以下は
、CPUとGPUの実行時間(Y軸)と入力数(X軸)の違いを示すグラフです。
スケジュール


次に、他のアプリケーションがロードされたプロセッサでテストすることにしました。アプリケーションで起動されたテストがプロセッサのリソースの55%を超えないように、プロセッサがロードされました。テスト結果を以下に示します。
スケジュール
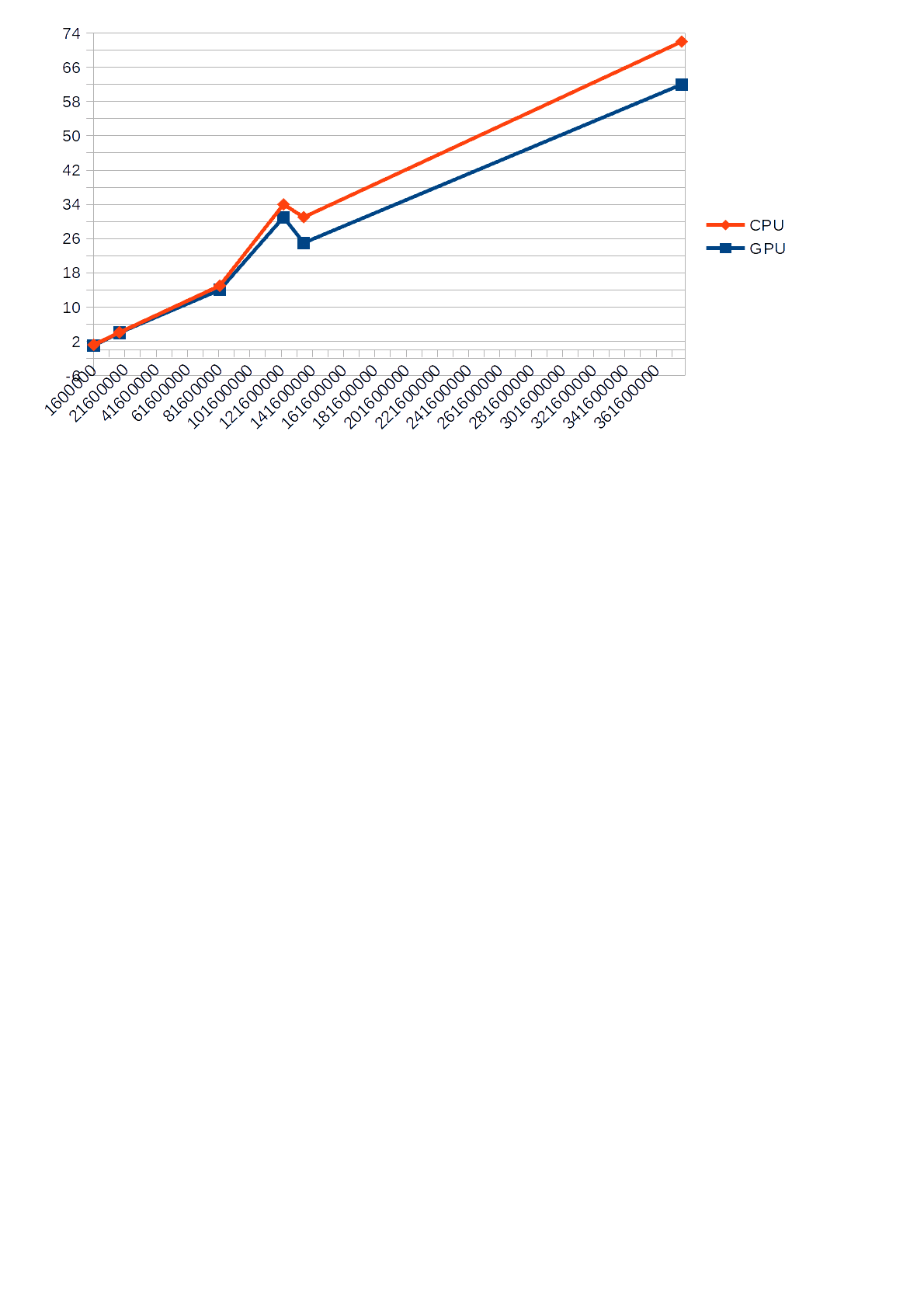

表からわかるように、CPUがロードされている場合、GPUで計算を実行すると、30%のプロセッサ負荷が55%の制限内に収まるため、パフォーマンスが向上します。計算にCPUを使用する場合、その負荷は68〜85%であり、 CPUに他のアプリケーションがロードされている場合、アルゴリズムの動作が遅くなります。
私の意見では、GPUがCPUに遅れをとっている理由は、CPUのコアパフォーマンスが高いためである可能性があります(3400 MHz CPU、1680 MHz GPU)。プロセッサコアに他のプロセスがロードされている場合、パフォーマンスは特定の時間間隔で処理されるスレッドの数に依存します。この場合、GPUはより多くのスレッド(1024 GPU、8 CPU)を同時に処理できるため、高速になります。
したがって、計算にGPUを使用しても、必ずしもアルゴリズムの動作が高速になる必要はないと結論付けることができますが、CPUをアンロードでき、他のアプリケーションがロードされている場合に役割を果たすことができます。