
クールなチャットモデレーターボットをPythonで書いてみましょう。彼がチャットをクリーンアップしたり、参加者を禁止して警告を発したり、新しいチャット参加者に挨拶したりできるようにします。
Telegramの限界と機能を考慮して、本格的なスケーラブルなボットを作成します。プロジェクト構造を作成し、簡単なコマンドに応答するようにボットに教えることから始めましょう。
Python , . Telethon Telegram API ( ) Databases SQLAlchemy Core ( ).

, , . BotFather.

. " 2077", — .
Telegram API
", -" , Telegram API Telegram Bot API.
Bot API : , . , Telegram API. , : , , - , - API. .
, Telegram API Telethon:
$ pip install telethon
Telegram API , my.telegram.org. , API .
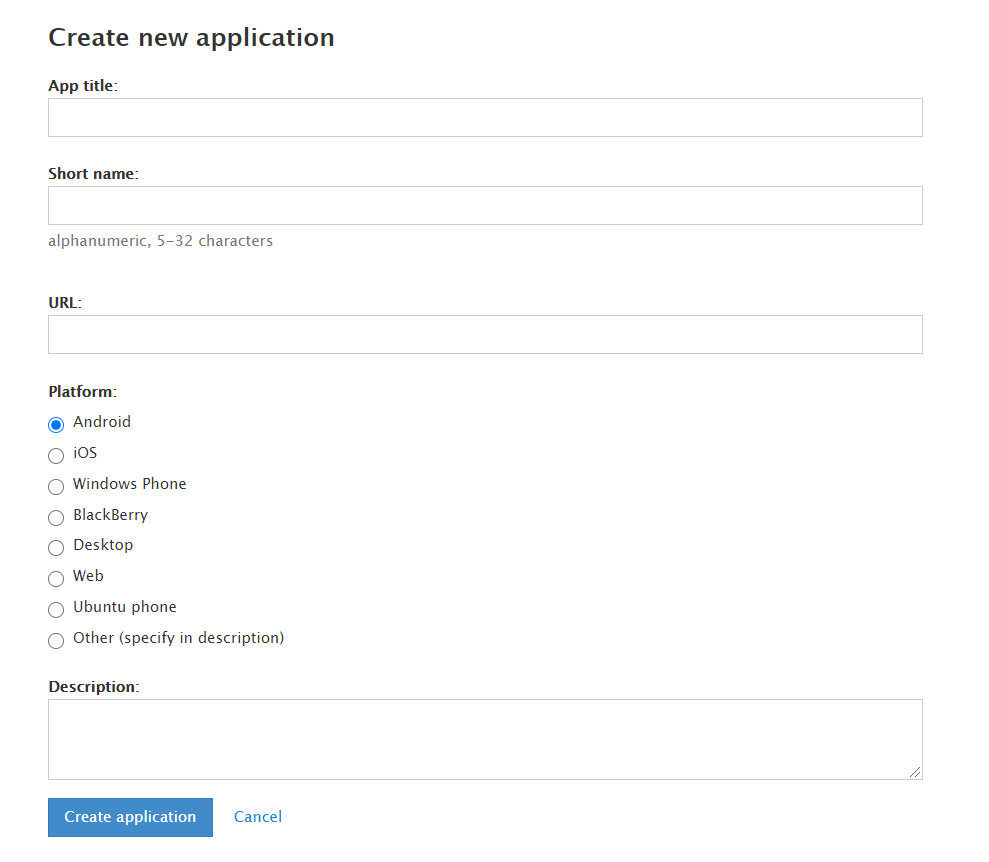
. api_id api_hash "". .
:
app/
__init__.py
__main__.py
handlers.py
config.py
handlers.py
— .
config.py
. :
BOT_TOKEN = '--'
API_ID = 123456789
API_HASH = '-'
, . config.
, __init__.py
. , telethon — TelegramClient
. .
( id, ). , TelegramClient:
import logging
from telethon import TelegramClient
import config
class Bot(TelegramClient):
def __init__(self, *args, **kwargs):
super().__init__(*args, **kwargs)
self.me = None #
# , API
bot = Bot('bot', config.API_ID, config.API_HASH)
. . ( 'bot'
: .)
parse_mode
— . ( , , ). HTML.
:
bot.parse_mode = 'HTML'
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
bot , : app.handlers ( ).
import app.handlers
, .
async def start():
#
await bot.connect()
# . sign_in . bot.me
bot.me = await bot.sign_in(bot_token=config.BOT_TOKEN)
#
await bot.run_until_disconnected()
, , run, start:
def run():
bot.loop.run_until_complete(start())
__init__.py
import logging
from telethon import TelegramClient
import config
class Bot(TelegramClient):
def __init__(self, *args):
super().__init__(*args)
self.me = None
bot = Bot('bot', config.API_ID, config.API_HASH)
bot.parse_mode = 'HTML'
logging.basicConfig(level=logging.INFO)
import app.handlers
async def start():
await bot.connect()
bot.me = await bot.sign_in(bot_token=config.BOT_TOKEN)
await bot.run_until_disconnected()
def run():
bot.loop.run_until_complete(start())
.
, handlers.py . .
? ( " ", " ", " " ). :
) ,
) , - ,
) ,
, . : ", !"
, telethon.events.ChatAction.
:
from telethon import events
from app import bot
@bot.on(events.ChatAction())
async def on_join(event: events.ChatAction.Event):
if event.is_group and event.user_added and event.user_id == bot.me.id:
await bot.send_message(event.chat.id, ', !')
@bot.on
. " ". , .
— __main__.py
run:
from app import run
run()
! .
$ python -m app
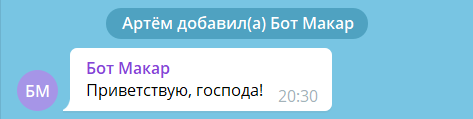
:
@bot.on(events.ChatAction(func=lambda e: e.is_group and e.user_added and e.user_id == bot.me.id))
async def on_join(event: events.ChatAction.Event):
await event.respond(', !')
ChatAction func
— . . .
event.respond
. , event. bot.send_message
, .
, , ! . :
, " ?":
...
from telethon.tl.custom import Message
...
@bot.on(events.NewMessage(func=lambda e: e.text.lower() == ' ?'))
async def who_are_you(event: Message):
await event.respond(' , , !')
Message — NewMessage.
--, privacy mode.
, /cat.
...
from telethon.tl.custom import Message
...
@bot.on(events.NewMessage(func=lambda e: e.text.lower() == '/cat'))
async def send_cat(event: Message):
await bot.send_message(event.chat.id, file='path/to/cat.png')
, /dice ( )
...
from telethon.tl.custom import Message
from telethon.tl.types import InputMediaDice
...
@bot.on(events.NewMessage(func=lambda e: e.text.lower() == '/dice'))
async def send_dice(event: Message):
await bot.send_message(event.chat.id, file=InputMediaDice('?'))

, , :
@bot.on(events.ChatAction(func=lambda e: (e.user_added or e.user_joined) and e.user_id != bot.me.id))
async def greet(event: events.ChatAction.Event):
await event.respond('!')
しかし、それが私たちがここに来た理由ではありません。グループ管理者向けのチームやその他の機能を作りたいです!これを行うには、管理者と通常のグループメンバーを区別できる必要があります。これについては、チュートリアルの次のパートで扱います。データベースを接続し、管理者を取得するための賢い方法を学びます。
つづく。
結果のコードはGitHubで表示できることを思い出してください。コメントで質問をしてください。きっと私か他の誰かが答えるでしょう。そして、記事の背景情報を提供してくれたvanutpに感謝します:)