コンテンツ
マハラノビスメトリックを使用する主な意味
1.用語と定義
2.2つのポイント間およびポイントとクラス間のマハラノビス距離
2.1。理論情報
2.2。2点間および点とクラス間の距離を計算するためのアルゴリズム
2.3。2点間および点とクラス
3間の距離の計算例。2つのクラス間のマハラノビス距離
3.1。理論情報
3.2。2つのクラス間の距離を計算するためのアルゴリズム
3.3。2つのクラス間の距離を計算する例
4.マハラノビス距離とk最近傍法
5.マハラノビスの加重距離
6.結論
コメントやエラーがある場合は、quwarm @ gmail.comまたはコメントに書き込んでください。
マハラノビス距離を使用する主なポイント
図1では、2つの観測値が赤い点で示されています。
クラスの中心は青い点で示されています。

問題は、どの観察がクラスの中心に近いかということです。
答えは、距離の測定方法によって異なります。
我々はに応じて距離を測定する場合は、ユークリッドメトリック、我々は、クラスの中心からの距離ことを得るポイントには
に等しくなる
点まで、
等しく
、それはある、ポイントは
近いクラスの中心に。
,
,
« » ,
.
, , .
1.
— , ,
— .
— :
,
—
.
—
:
.
,
—
.
«» - . .
-. - — , .
:
.
, (-) .
2.
( ) ( ) .
2.1
—
, ( )
:
,
, .
, .
, ( 1) ( 0) , .
-.
( [internet archive] ), . .
:
1. : ;
2. : ;
3. : .
: .
, 0, 0 (max(0.0, value)
) NaN, ( sqrt
0.5
) 0 (, ). .
, — .
( ) , — ( ) (. . « »).
, . , .
(, - , . 4) , .
, , * .
*
:
—
,
—
,
—
.
:
— — ( , . «sample covariance»):
—
,
—
.
,
. , ( , . «population covariance»):
:
() ,
;
,
( ),
;
,
( *).
:
.
— :
.
*
—
.
, :
— .
2.
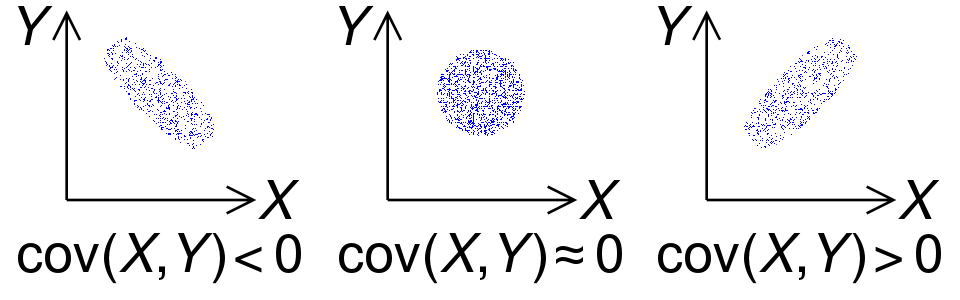
, , ( ), ,
. .
, :
1. - , ,
.
: .
2. (, «perfect covariance»). :
— ;
— .
3.
:
.
1.
, ( — )
.
.
3.
4.
(shrinkage) — (. . ).
,
— ,
— ,
,
.
:
Olivier Ledoit Michael Wolf — ,
—
, ,
— ,
.
, , Python scikit-learn (sklearn.covariance.LedoitWolf, sklearn.covariance.ledoit_wolf, sklearn.covariance.ledoit_wolf_shrinkage).
. 8 , « , , » ( ). — ( ,
, ) , .
.
, ( Python):
— ;
—
:
;
—
:
;
—
:
;
—
:
.
:
—
.
Shrunk Covariance (sklearn.covariance.ShrunkCovariance, sklearn.covariance.shrunk_covariance). , (
).
( Ledoit — Wolf): .
, LedoitWolf ShrunkCovariance ( ) empirical_covariance, (. «population covariance», ).
5.
( ), « »:
— (
/
)
( , «corrected sample standard deviation»):
—
/
)
.
:
,
. , ( , . «uncorrected sample standard deviation»):
- .
, .
, , 10 , . , , , .
2.2
1. .
2. .
3. .
4. , . , .
2.3
(. 3):
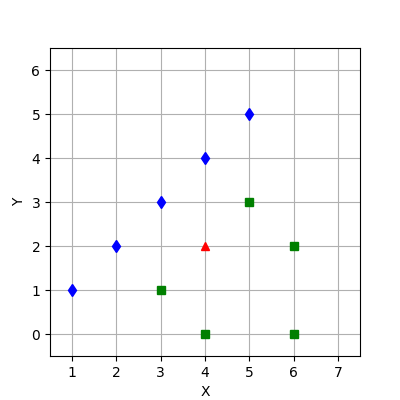
1. .
2. .
:
:
3. .
.
:
: . ,
.
.
:
: . ,
.
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
classes = [
np.array([[1, 1], [2, 2], [3, 3], [4, 4], [5, 5]]),
np.array([[3, 1], [4, 0], [6, 0], [6, 2], [5, 3]])
]
centroids = [class_.mean(axis=0) for class_ in classes]
standard_deviations = [class_.std(axis=0, ddof=1) for class_ in classes]
covariance_matrices = np.array([np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=1) for class_ in classes])
det_covariance_matrices = [np.linalg.det(cov) for cov in covariance_matrices]
print("Centroids:", *centroids)
print("Standard deviations:", *standard_deviations)
print("Covariance matrices:", *covariance_matrices.tolist())
print("Determinants of covariance matrices:", det_covariance_matrices)
:
Centroids: [3. 3.] [4.8 1.2] Standard deviations: [1.58113883 1.58113883] [1.30384048 1.30384048] Covariance matrices: [[2.5, 2.5], [2.5, 2.5]] [[1.7, 0.3], [0.3, 1.7]] Determinants of covariance matrices: [0.0, 2.8]
4. , — . , .
, , , .
, .
. — , 5 : (1) — , (2) (LedoitWolf), (3) , (4) , (5) — :
1. — .
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
def mahalanobis(point_from, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix):
delta = point_from - point_to
return max(np.float64(0), np.dot(np.dot(delta, inverse_covariance_matrix), delta)) ** 0.5
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]])
covariance_matrix = np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=1)
inverse_covariance_matrix = np.linalg.inv(covariance_matrix + np.identity(covariance_matrix.shape[0]))
print(" :\n", inverse_covariance_matrix, sep='')
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_E-M (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", (COV+E)^(-1)) = ",
mahalanobis(test_point, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix), sep='')
:
: [[ 0.58333333 -0.41666667] [-0.41666667 0.58333333]] d_E-M ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.414213562373095 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [1. 1.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.8257418583505538 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [2. 2.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.5275252316519465 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.414213562373095 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [4. 4.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.5275252316519465 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [5. 5.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.8257418583505536
— , .
2. (LedoitWolf).
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5 scikit-learn 0.24.1
import numpy as np
from sklearn.covariance import LedoitWolf
def mahalanobis(point_from, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix):
delta = point_from - point_to
return max(np.float64(0), np.dot(np.dot(delta, inverse_covariance_matrix), delta)) ** 0.5
def approx(number, *, sign, epsilon=1e-4):
return number + np.sign(sign) * epsilon
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]])
lw = LedoitWolf().fit(class_)
lw_covariance_matrix = lw.covariance_
lw_lambda = lw.shrinkage_
covariance_matrix = np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=0)
mu = np.sum(np.trace(covariance_matrix)) / class_.shape[0]
T = mu * np.identity(class_.shape[1])
print("T:", *T)
print("COV(*):", *lw_covariance_matrix)
print("Lambda:", lw_lambda)
# - T
# ( : T )
# ddof=0, . . LedoitWolf empirical_covariance (. )
first_condition = (np.linalg.eig(T)[0] > approx(0., sign=+1)).all()
print("All(", np.linalg.eig(T)[0], ") > 0 ? -> ", first_condition, sep='')
# - (0, 1]
second_condition = approx(0., sign=+1) < lw_lambda <= 1
print("Lambda =", lw_lambda, "in (0, 1] ? ->", second_condition)
# - COV(*)
# lambda, T
cov_eig = min(np.linalg.eig(lw_covariance_matrix)[0])
lambda_t_eig = lw_lambda * min(np.linalg.eig(T)[0])
third_condition = cov_eig >= lambda_t_eig
print(cov_eig, ">=", lambda_t_eig, "? ->", third_condition)
conditions = [first_condition, second_condition, third_condition]
if all(conditions):
print(" ")
#
inverse_lw_covariance_matrix = np.linalg.inv(lw_covariance_matrix)
print(" :\n", inverse_lw_covariance_matrix, sep='')
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_M(*) (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", COV(*)) = ",
mahalanobis(test_point, point_to, inverse_lw_covariance_matrix), sep='')
else:
print(" (1-3): ", [i for i, x in enumerate(conditions, 1) if not x])
:
T: [0.8 0. ] [0. 0.8] COV(*): [2. 1.44] [1.44 2. ] Lambda: 0.27999999999999997 All([0.8 0.8]) > 0 ? -> True Lambda = 0.27999999999999997 in (0, 1] ? -> True 0.56 >= 0.22399999999999998 ? -> True : [[ 1.03820598 -0.74750831] [-0.74750831 1.03820598]] d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], COV(*)) = 1.889822365046136 d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [1. 1.], COV(*)) = 2.4283759936997833 d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [2. 2.], COV(*)) = 2.037847864848056 d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], COV(*)) = 1.889822365046136 d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [4. 4.], COV(*)) = 2.037847864848056 d_M(*) ([4. 2.], [5. 5.], COV(*)) = 2.4283759936997833
— , .
3. .
. .
, — .
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
def mahalanobis(point_from, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix):
delta = point_from - point_to
return max(np.float64(0), np.dot(np.dot(delta, inverse_covariance_matrix), delta)) ** 0.5
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]])
covariance_matrix = np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=1)
# (Singular Value Decomposition, SVD)
#
pseudo_inverse_covariance_matrix = np.linalg.pinv(covariance_matrix)
print(" :\n", pseudo_inverse_covariance_matrix, sep='')
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_M+ (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", COV+) = ",
mahalanobis(test_point, point_to, pseudo_inverse_covariance_matrix), sep='')
:
: [[0.1 0.1] [0.1 0.1]] d_M+ ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], COV+) = 0.0 d_M+ ([4. 2.], [1. 1.], COV+) = 1.2649110640673513 d_M+ ([4. 2.], [2. 2.], COV+) = 0.6324555320336757 d_M+ ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], COV+) = 0.0 d_M+ ([4. 2.], [4. 4.], COV+) = 0.6324555320336757 d_M+ ([4. 2.], [5. 5.], COV+) = 1.2649110640673513
— , .
4. .
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
def euclid_std(point_from, point_to, standard_deviations):
return sum(((point_from - point_to) / standard_deviations) ** 2) ** 0.5
def approx(number, *, sign, epsilon=1e-4):
return number + np.sign(sign) * epsilon
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]])
standard_deviations = class_.std(axis=0, ddof=1)
# 0
std_le_0 = standard_deviations <= approx(0., sign=+1, epsilon=1e-6)
print(" :\n", standard_deviations, sep='')
if std_le_0.any():
print(" 0: ", np.where(std_le_0)[0])
else:
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_std (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", sigma) = ",
euclid_std(test_point, point_to, standard_deviations), sep='')
:
: [1.58113883 1.58113883] d_std ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], sigma) = 0.8944271909999159 d_std ([4. 2.], [1. 1.], sigma) = 1.9999999999999998 d_std ([4. 2.], [2. 2.], sigma) = 1.2649110640673518 d_std ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], sigma) = 0.8944271909999159 d_std ([4. 2.], [4. 4.], sigma) = 1.2649110640673518 d_std ([4. 2.], [5. 5.], sigma) = 1.9999999999999998
— , .
5. .
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
def euclid_std(point_from, point_to, standard_deviations):
return sum(((point_from - point_to) / standard_deviations) ** 2) ** 0.5
def euclid_diag(point_from, point_to, standard_deviations):
return euclid_std(point_from, point_to, standard_deviations) \
* (np.prod(standard_deviations ** 2)) ** (1. / point_from.shape[0])
def approx(number, *, sign, epsilon=1e-4):
return number + np.sign(sign) * epsilon
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]])
standard_deviations = class_.std(axis=0, ddof=1)
# 0
std_le_0 = standard_deviations <= approx(0., sign=+1, epsilon=1e-6)
print(" :\n", standard_deviations, sep='')
if std_le_0.any():
print(" 0: ", np.where(std_le_0)[0])
else:
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_diag (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", sigma) = ",
euclid_diag(test_point, point_to, standard_deviations), sep='')
:
: [1.58113883 1.58113883] d_diag ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], sigma) = 2.2360679774997902 d_diag ([4. 2.], [1. 1.], sigma) = 5.0 d_diag ([4. 2.], [2. 2.], sigma) = 3.16227766016838 d_diag ([4. 2.], [3. 3.], sigma) = 2.2360679774997902 d_diag ([4. 2.], [4. 4.], sigma) = 3.16227766016838 d_diag ([4. 2.], [5. 5.], sigma) = 5.0
— , .
—
,
— .
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
import numpy as np
def mahalanobis(point_from, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix):
delta = point_from - point_to
return max(np.float64(0), np.dot(np.dot(delta, inverse_covariance_matrix), delta)) ** 0.5
def approx(number, *, sign, epsilon=1e-4):
return number + np.sign(sign) * epsilon
test_point = np.array([4., 2.])
class_ = np.array([[3., 1.], [4., 0.], [6., 0.], [6., 2.], [5., 3.]])
covariance_matrix = np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=1)
if abs(np.linalg.det(covariance_matrix)) <= approx(0., sign=+1):
print(" 0. .")
else:
inverse_covariance_matrix = np.linalg.inv(covariance_matrix)
print(" (d_M):\n", inverse_covariance_matrix, sep='')
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_M (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", COV^(-1)) = ",
mahalanobis(test_point, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix), sep='')
covariance_matrix = covariance_matrix + np.identity(class_.shape[1])
inverse_covariance_matrix = np.linalg.inv(covariance_matrix)
print(" (d_E-M):\n", inverse_covariance_matrix, sep='')
for point_to in [class_.mean(axis=0), *class_]:
print("d_E-M (", test_point, ", ", point_to, ", (COV+E)^(-1)) = ",
mahalanobis(test_point, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix), sep='')
:
(d_M): [[ 0.60714286 -0.10714286] [-0.10714286 0.60714286]] d_M ([4. 2.], [4.8 1.2], COV^(-1)) = 0.9561828874675149 d_M ([4. 2.], [3. 1.], COV^(-1)) = 1.0 d_M ([4. 2.], [4. 0.], COV^(-1)) = 1.5583874449479593 d_M ([4. 2.], [6. 0.], COV^(-1)) = 2.3904572186687876 d_M ([4. 2.], [6. 2.], COV^(-1)) = 1.5583874449479593 d_M ([4. 2.], [5. 3.], COV^(-1)) = 1.0 (d_E-M): [[ 0.375 -0.04166667] [-0.04166667 0.375 ]] d_E-M ([4. 2.], [4.8 1.2], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 0.7302967433402214 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [3. 1.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 0.8164965809277259 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [4. 0.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.224744871391589 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [6. 0.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.8257418583505536 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [6. 2.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 1.224744871391589 d_E-M ([4. 2.], [5. 3.], (COV+E)^(-1)) = 0.8164965809277259
— .
•
:
1. — : ;
2. (LedoitWolf): ;
3. : ;
4. : ;
5. : .
( ): .
( — ): .
3, ( ) — , .
•
:
1. — : ;
2. (LedoitWolf): ;
3. : ;
4. : ;
5. : .
( ): .
( — ): .
3, ( ) .
•
:
1. — : ;
2. (LedoitWolf): ;
3. : ;
4. : ;
5. : .
( ): .
( — ): .
3, ( ) — , .
.
3.
( ) .
3.1
—
:
— ,
— ,
— ,
— .
:
.
, , .
, , ( ) (. 2 « »):
- :
— ,
.
3.2
1. .
2. .
3. , .
4. , . , — .
3.3
. 2.2.
.
3 . 2.2.
4 .
4. , . , — .
:
:
•
.
— .
:
— ;
— — .
•
.
—
.
:
—
;
— —
.
•
.
—
.
:
—
;
— —
.
4. k-
- . ,
- ( )
.
- .
:
— : ( — );
— ( , ).
Python 3.6 numpy 1.19.5
#
import heapq
from collections import Counter
from operator import itemgetter
import numpy as np
class MkNN:
def __init__(self, k, classes, inv_cov_matrices):
self.n = len(classes)
self.k = k
self.classes = classes
self.inv_cov_matrices = inv_cov_matrices
@staticmethod
def mahalanobis_sqr(point_from, point_to, inverse_covariance_matrix):
delta = point_from - point_to
return max(np.float64(0), np.dot(np.dot(delta, inverse_covariance_matrix), delta))
def _get_k_smallest(self, test_point):
generator = (
(MkNN.mahalanobis_sqr(test_point, point, inv_cov), i)
for i, (class_, inv_cov) in enumerate(zip(self.classes, self.inv_cov_matrices))
for point in class_
)
return heapq.nsmallest(self.k, generator, key=itemgetter(0))
def predict(self, test_point):
return heapq.nlargest(1, Counter((i for _, i in self._get_k_smallest(test_point))).items(),
key=lambda t: (t[1], -t[0]))[0][0]
def predict_proba(self, test_point):
most_common = Counter((i for _, i in self._get_k_smallest(test_point)))
classes_proba = np.array([most_common.get(i, 0) for i in range(self.n)])
return classes_proba / classes_proba.sum()
def predict_all_max(self, test_point):
p = self.predict_proba(test_point)
return np.where(p == max(p))[0]
def main():
# , - classes
test_points = np.array([[4., 2.]])
#
classes = [
np.array([[1., 1.], [2., 2.], [3., 3.], [4., 4.], [5., 5.]]),
np.array([[3., 1.], [4., 0.], [6., 0.], [6., 2.], [5., 3.]])
]
#
n_train_points = sum(class_.shape[0] for class_ in classes)
#
cov_matrices = [np.cov(class_, rowvar=False, ddof=1) for class_ in classes]
# -- -
inv_cov_matrices = [np.linalg.inv(cov + np.identity(cov.shape[0])) for cov in cov_matrices]
for test_point in test_points:
print("Point:", test_point)
# k 1 ( )
for i in range(1, n_train_points):
classifier = MkNN(i, classes, inv_cov_matrices)
print(f"{i}nn:",
1 + classifier.predict(test_point),
classifier.predict_proba(test_point),
classifier.predict_all_max(test_point))
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
:
"knn: [ ( 1), ] [ ] [ ( 0), ]".
Point: [4. 2.] 1nn: 2 [0. 1.] [1] 2nn: 2 [0. 1.] [1] 3nn: 2 [0. 1.] [1] 4nn: 2 [0. 1.] [1] 5nn: 2 [0.2 0.8] [1] 6nn: 2 [0.33333333 0.66666667] [1] 7nn: 2 [0.42857143 0.57142857] [1] 8nn: 1 [0.5 0.5] [0 1] 9nn: 2 [0.44444444 0.55555556] [1]
. 4.

Python 3.6
# ...
from operator import sub
import numpy as np # 1.19.5
from matplotlib import colors, pyplot as plt # 3.3.4
#
def show_data_on_mesh(k, classes, inv_cov_matrices):
#
min_ = np.min([np.min(class_, axis=0) for class_ in classes], axis=1) - 1
max_ = np.max([np.max(class_, axis=0) for class_ in classes], axis=1) + 1
min_c = min(min_[0], min_[1])
max_c = max(max_[0], max_[1])
h = 0.05
test_mesh = np.meshgrid(np.arange(min_c, max_c, h), np.arange(min_c, max_c, h))
test_points = np.c_[test_mesh[0].ravel(), test_mesh[1].ravel()]
#
classifier = MkNN(k, classes, inv_cov_matrices)
test_mesh_labels = [sub(*classifier.predict_proba(x)) for x in test_points]
#
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 5), dpi=90)
class_colormap = colors.ListedColormap(['#070648', '#480607'])
plt.pcolormesh(test_mesh[0], test_mesh[1],
np.asarray(test_mesh_labels).reshape(test_mesh[0].shape),
cmap='coolwarm', shading='nearest')
plt.colorbar()
plt.scatter([point[0] for class_ in classes for point in class_],
[point[1] for class_ in classes for point in class_],
c=[-i for i, class_ in enumerate(classes) for _ in class_],
cmap=class_colormap)
plt.axis([min_c, max_c, min_c, max_c])
plt.xlabel("X")
plt.ylabel("Y")
plt.title("k=" + str(k))
plt.show()
# ...
— .
5.
, — , :
( , ) :
— :
6.
, ( ) , - — .
?
1. , .
2. «Metric Learning» (: Aurélien Bellet, Amaury Habrard, Marc Sebban; ).
3. (, k-means: 1, 2, 3).
4. ().
5. ( 1, 記事2、記事3)。
コメントやエラーがある場合は、quwarm @ gmail.comまたはコメントに書き込んでください。