
前書き
非同期プログラミングは一種の並列プログラミングであり、メインのアプリケーション実行スレッドとは別に作業単位を実行できます。作業が完了すると、ワークフローの完了またはエラーの発生がメインスレッドに通知されます。このアプローチには、アプリケーションのパフォーマンスの向上や応答性の向上など、多くの利点があります。
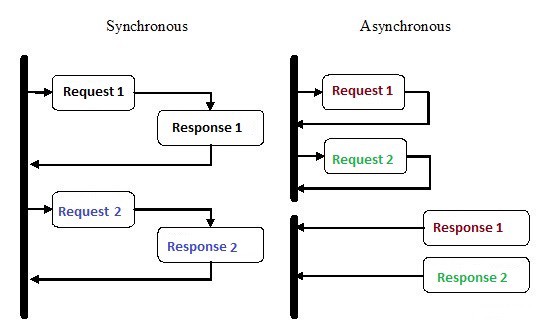
非同期プログラミングはここ数年、多くの注目を集めていますが、それには十分な理由があります。この種のプログラミングは、従来の順次実行よりも複雑になる可能性がありますが、はるかに効率的です。
たとえば、HTTPリクエストが完了するのを待ってから実行を続行する代わりに、リクエストを送信して、Pythonの非同期コルーチンを使用してインラインで待機している他の作業を行うことができます。
非同期は、バックエンドの実装でNode.jsが普及する主な理由の1つです。特にWebサイトなど、I / Oが重いアプリケーションで作成する大量のコードは、外部リソースに依存しています。これには、リモートデータベース呼び出しからPOST要求、RESTサービスまで、何でも含めることができます。これらのリソースの1つにリクエストを送信するとすぐに、コードは応答を待ちます。非同期プログラミングでは、リソースからの応答を待つ間、コードで他のタスクを処理できます。
Pythonはどのようにして同時に複数のことを行うのですか?
1.複数のプロセス
最も明白な方法は、複数のプロセスを使用することです。ターミナルからスクリプトを2、3、4、10回実行すると、すべてのスクリプトが独立して同時に実行されます。オペレーティングシステムは、すべてのインスタンス間でのプロセッサリソースの分散を処理します。または、以下の例に示すように、複数のプロセスを生成できるマルチプロセッシングライブラリを使用することもできます。
from multiprocessing import Process
def print_func(continent='Asia'):
print('The name of continent is : ', continent)
if __name__ == "__main__": # confirms that the code is under main function
names = ['America', 'Europe', 'Africa']
procs = []
proc = Process(target=print_func) # instantiating without any argument
procs.append(proc)
proc.start()
# instantiating process with arguments
for name in names:
# print(name)
proc = Process(target=print_func, args=(name,))
procs.append(proc)
proc.start()
# complete the processes
for proc in procs:
proc.join()出力:
The name of continent is : Asia
The name of continent is : America
The name of continent is : Europe
The name of continent is : Africa2.複数のスレッド
複数のジョブを並行して実行するもう1つの方法は、スレッドを使用することです。スレッドは実行キューであり、プロセスとよく似ていますが、単一のプロセスに複数のスレッドを含めることができ、それらすべてがリソースを共有します。ただし、これにより、ストリームコードの記述が難しくなります。同様に、オペレーティングシステムはプロセッサメモリの割り当てというハードワークをすべて実行しますが、グローバルインタープリターロック(GIL)では、マルチスレッドコードがある場合でも、1つの単位時間で実行できるPythonスレッドは1つだけです。したがって、CPythonのGILはマルチコアの競争力を妨げます。つまり、2つ、4つ、またはそれ以上のコアがある場合でも、強制的に実行できるコアは1つだけです。
import threading
def print_cube(num):
"""
function to print cube of given num
"""
print("Cube: {}".format(num * num * num))
def print_square(num):
"""
function to print square of given num
"""
print("Square: {}".format(num * num))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# creating thread
t1 = threading.Thread(target=print_square, args=(10,))
t2 = threading.Thread(target=print_cube, args=(10,))
# starting thread 1
t1.start()
# starting thread 2
t2.start()
# wait until thread 1 is completely executed
t1.join()
# wait until thread 2 is completely executed
t2.join()
# both threads completely executed
print("Done!")出力:
Square: 100
Cube: 1000
Done!3.コルーチンと
yield:
コルーチンは、ルーチンの一般化です。これらは、協調的マルチタスクに使用されます。このプロセスでは、プロセスが任意の
yield頻度で、または複数のアプリケーションを同時に実行できるように待機している間に、自発的に制御()を引き渡します。コルーチンはジェネレーターに似ていますが、メソッドが追加され、yieldステートメントの使用方法が若干変更されています。ジェネレーターは反復用のデータを生成しますが、コルーチンはデータを消費することもできます。
def print_name(prefix):
print("Searching prefix:{}".format(prefix))
try :
while True:
# yeild used to create coroutine
name = (yield)
if prefix in name:
print(name)
except GeneratorExit:
print("Closing coroutine!!")
corou = print_name("Dear")
corou.__next__()
corou.send("James")
corou.send("Dear James")
corou.close()出力:
Searching prefix:Dear
Dear James
Closing coroutine!!4.非同期プログラミング
4番目の方法は、オペレーティングシステムが関与しない非同期プログラミングです。オペレーティングシステム側では、スレッドが1つしかないプロセスが1つありますが、同時に複数のタスクを実行できます。だからここでのトリックは何ですか?
回答:
asyncio
Asyncio-Python 3.4で導入された非同期プログラミングモジュール。コルーチンとフューチャーを使用して非同期コードを簡単に記述できるように設計されており、コールバックがないため、同期コードとほぼ同じくらい読みやすくなっています。
Asyncio異なるデザインを使用します:、event loopコルーチン、およびfuture。
- event loop . .
- ( ) – , Python, await event loop. event loop. Tasks, Future.
- Future , . exception.
ヘルプを使用すると、
asyncioサブタスクがコルーチンとして定義されるようにコードを構造化し、サブタスクを同時に実行するようにスケジュールすることができます。コルーチンにはyield、可能なコンテキスト切り替えポイントを定義するポイントが含まれています。待機キューにタスクがある場合、コンテキストは切り替えられますが、そうでない場合は切り替えられません。
コンテキストスイッチ
asyncioはevent loop、1つのコルーチンから別のコルーチンに制御フローを転送するものです。
次の例では、3つの非同期タスクを開始します。これらのタスクは、Redditに個別にリクエストを出し、JSONのコンテンツを抽出して表示します。aiohttpを使用しています -HTTPリクエストであっても非同期で行われるようにするhttpクライアントライブラリ。
import signal
import sys
import asyncio
import aiohttp
import json
loop = asyncio.get_event_loop()
client = aiohttp.ClientSession(loop=loop)
async def get_json(client, url):
async with client.get(url) as response:
assert response.status == 200
return await response.read()
async def get_reddit_top(subreddit, client):
data1 = await get_json(client, 'https://www.reddit.com/r/' + subreddit + '/top.json?sort=top&t=day&limit=5')
j = json.loads(data1.decode('utf-8'))
for i in j['data']['children']:
score = i['data']['score']
title = i['data']['title']
link = i['data']['url']
print(str(score) + ': ' + title + ' (' + link + ')')
print('DONE:', subreddit + '\n')
def signal_handler(signal, frame):
loop.stop()
client.close()
sys.exit(0)
signal.signal(signal.SIGINT, signal_handler)
asyncio.ensure_future(get_reddit_top('python', client))
asyncio.ensure_future(get_reddit_top('programming', client))
asyncio.ensure_future(get_reddit_top('compsci', client))
loop.run_forever()出力:
50: Undershoot: Parsing theory in 1965 (http://jeffreykegler.github.io/Ocean-of-Awareness-blog/individual/2018/07/knuth_1965_2.html)
12: Question about best-prefix/failure function/primal match table in kmp algorithm (https://www.reddit.com/r/compsci/comments/8xd3m2/question_about_bestprefixfailure_functionprimal/)
1: Question regarding calculating the probability of failure of a RAID system (https://www.reddit.com/r/compsci/comments/8xbkk2/question_regarding_calculating_the_probability_of/)
DONE: compsci
336: /r/thanosdidnothingwrong -- banning people with python (https://clips.twitch.tv/AstutePluckyCocoaLitty)
175: PythonRobotics: Python sample codes for robotics algorithms (https://atsushisakai.github.io/PythonRobotics/)
23: Python and Flask Tutorial in VS Code (https://code.visualstudio.com/docs/python/tutorial-flask)
17: Started a new blog on Celery - what would you like to read about? (https://www.python-celery.com)
14: A Simple Anomaly Detection Algorithm in Python (https://medium.com/@mathmare_/pyng-a-simple-anomaly-detection-algorithm-2f355d7dc054)
DONE: python
1360: git bundle (https://dev.to/gabeguz/git-bundle-2l5o)
1191: Which hashing algorithm is best for uniqueness and speed? Ian Boyd's answer (top voted) is one of the best comments I've seen on Stackexchange. (https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/49550/which-hashing-algorithm-is-best-for-uniqueness-and-speed)
430: ARM launches “Facts” campaign against RISC-V (https://riscv-basics.com/)
244: Choice of search engine on Android nuked by “Anonymous Coward” (2009) (https://android.googlesource.com/platform/packages/apps/GlobalSearch/+/592150ac00086400415afe936d96f04d3be3ba0c)
209: Exploiting freely accessible WhatsApp data or “Why does WhatsApp web know my phone’s battery level?” (https://medium.com/@juan_cortes/exploiting-freely-accessible-whatsapp-data-or-why-does-whatsapp-know-my-battery-level-ddac224041b4)
DONE: programming使用RedisのとRedisのキューRQ
とを使用することは、特に古いバージョンのPythonを使用している場合は、常に良い
asyncioとはaiohttp限りません。さらに、異なるサーバー間でタスクを分散する必要がある場合があります。この場合、RQ(Redis Queue)を使用できます。これは、ジョブをキューに追加し、バックグラウンドでワーカーが処理するための一般的なPythonライブラリです。キューを整理するために、Redisが使用されます-キー/値のデータベース。
以下の例では、
count_words_at_urlRedisを使用してキューに単純な関数を追加しました。
from mymodule import count_words_at_url
from redis import Redis
from rq import Queue
q = Queue(connection=Redis())
job = q.enqueue(count_words_at_url, 'http://nvie.com')
******mymodule.py******
import requests
def count_words_at_url(url):
"""Just an example function that's called async."""
resp = requests.get(url)
print( len(resp.text.split()))
return( len(resp.text.split()))出力:
15:10:45 RQ worker 'rq:worker:EMPID18030.9865' started, version 0.11.0
15:10:45 *** Listening on default...
15:10:45 Cleaning registries for queue: default
15:10:50 default: mymodule.count_words_at_url('http://nvie.com') (a2b7451e-731f-4f31-9232-2b7e3549051f)
322
15:10:51 default: Job OK (a2b7451e-731f-4f31-9232-2b7e3549051f)
15:10:51 Result is kept for 500 seconds結論
例として、最高のチェスプレーヤーの1人が多数の人々と競争するチェスの展示会を考えてみましょう。私たちには24のゲームと24人のユーザーがいて、チェスプレーヤーがそれらと同期してプレイする場合、少なくとも12時間かかります(平均的なゲームが30ハンドかかると仮定すると、チェスプレーヤーは5秒以内に1ハンドを考え、対戦相手は約55秒かかります。)ただし、非同期モードでは、チェスプレーヤーは次の対戦相手に移動してその動きを分割しながら、移動して相手が考える時間を残すことができます。したがって、2分間で24のゲームすべてに移動でき、1時間ですべて勝ちます。
これは、非同期性により物事がより速くなると人々が言うときに暗示されるものです。私たちはそのようなスピードについて話している。優れたチェスプレーヤーは、チェスのプレイを速く開始するのではなく、時間をより最適化し、待機するのに無駄にしないだけです。これがどのように機能するかです。
この例えで言うと、チェスプレーヤーはプロセッサであり、主なアイデアは、プロセッサをできるだけ短い時間アイドル状態に保つことです。事は彼がいつもレッスンをしたということです。
実際には、非同期は並列プログラミングのスタイルとして定義されており、他のタスクがそれを利用できるように、一部のタスクは待機中にプロセッサを解放します。要件、コードフロー、データ処理、アーキテクチャ、およびユースケースを満たすPythonで並行性を実現する方法はいくつかあり、それらのいずれかを選択できます。
.